For all GST queries, Please contact: 1800 599 5399 / 040 23230583 / 7901 243 117 / 7901 243 172
Home »
About Us
Useful Websites
GST & Customs Commissionerates of Hyderabad GST Zone
About Us
Welcome to Hyderabad GST Zone
The Government of India has introduced the Central Excises and Salt Act 1944 w.e.f. 24.2.1944 for the collection of Excise duty on the manufacture of goods, including tax on salt. In the year 1962, the Government of India has introduced a levy of Customs on imports and exports through the enactment of the Customs Act, 1962. For collection and administration of Central Excise and Customs, the Government of India created a separate Board, the Central Board of Excise and Customs(CBEC) in 1964 under the Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finance, through the Central Boards of Revenue Act, 1963. Later, in 1994, the Government of India introduced a levy of Service Tax on certain services. The indirect taxes are a major source of revenue, contributing 35 to 40% of revenue to the exchequer.
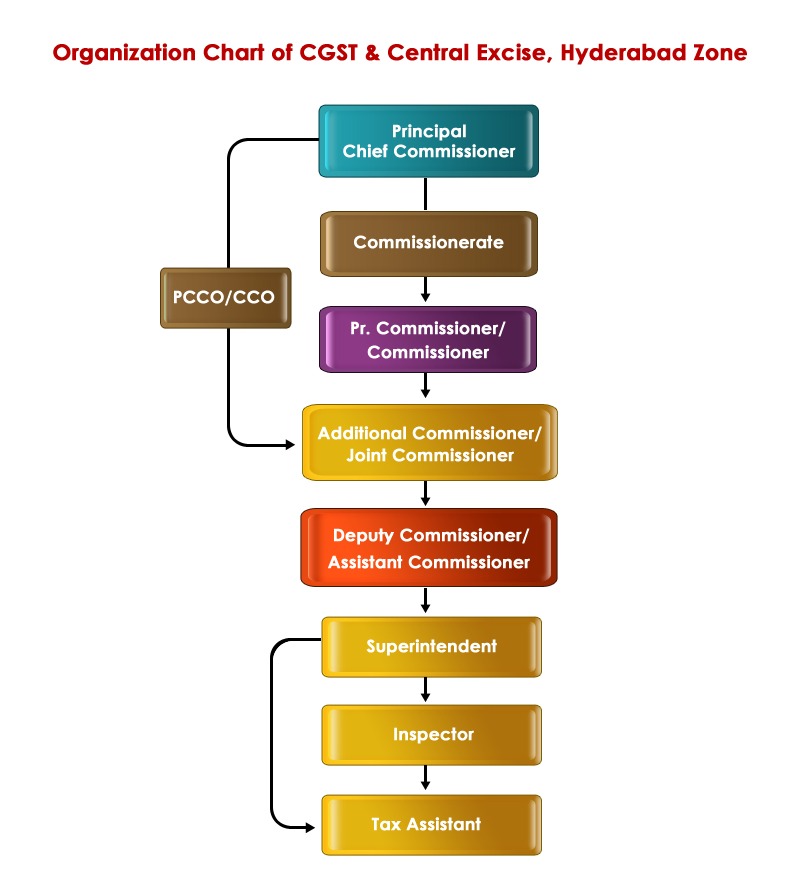
For the collection of indirect taxes, the Central Board of Excise & Customs has formed several Collectorates (now Commissionerates) headed by a Collector (now Commissioner) with field formations of Divisions/Ranges/Sectors/Circles headed by an Assistant Collector (now Assistant Commissioner). The Hyderabad Collectorate was formed 70 years back, covering the entire undivided State of Andhra Pradesh.
The Central Board of Excise and Customs has reviewed the requirement of manpower from time to time and restructured the cadres by revising the sanctioned strength from time to time. The Guntur Collectorate (now Guntur Commissionerate) was formed in the year 1972 and the Visakhapatnam Collectorate (now Visakhapatnam Commissionerate) in 1990. All the Commissionerates of erstwhile Hyderabad, Guntur, and Vishakhapatnam Commissionerates were under a single zone. Consequent to cadre restructuring in 2002, two zones were formed: (i) (i) Hyderabad Zone, covering all the districts of the Telangana region, and (ii) Visakhapatnam Zone, covering the remaining districts of Rayalaseema and the coastal districts of erstwhile Andhra Pradesh. Again, CBEC has reviewed the requirement of manpower and restructured the cadres in the year 2014 (incidentally, the State of Andhra Pradesh was divided into two states, viz., Telangana and Andhra Pradesh, in the same year) by creating the separate Commissionerates of Customs, Service Tax, and Audit in Hyderabad Zone. The Government of India has introduced the Goods and Services Tax from 01.07.2017 by replacing the existing indirect taxes, including Central Excise, Service Tax, VAT, etc. Accordingly, CBEC has reorganised its formations. Further, the Central Board of Excise & Customs (CBEC) has also been renamed as the Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC). At present, CBIC has 21 Zones, 101 GST taxpayer services Commissionerates comprising 15 Sub-commissionerates, 768 Divisions, 3969 Ranges, 49 Audit Commissionerates and 50 Appeals commissionerates. This will ensure rendering of taxpayer services to all the taxpayers through an indirect tax administration structure, having a pan-India presence.
Consequent to GST implementation w.e.f. 01.07.2017, Hyderabad Zone comprises 04 GST Executive Commissionerates, viz., Hyderabad, Medchal, Secunderabad and Rangareddy; 02 Audit Commissionerates, viz., Audit - I and Audit - II; and 02 Appeals Commissionerates, viz., Appeals - I and Appeals - II, in addition to the Hyderabad Customs Commissionerate. The Chief Commissioner’s Office of GST & Customs, Hyderabad Zone, is located at GST Bhavan, Basheerbagh, Hyderabad, having its jurisdiction over the entire State of Telangana for the collection of Customs & Indirect Taxes. The Zone is headed by a (Principal) Chief Commissioner.
Shri Sanjay Rathi, IRS, is presently the Principal Chief Commissioner of the Hyderabad GST & Customs Zone.